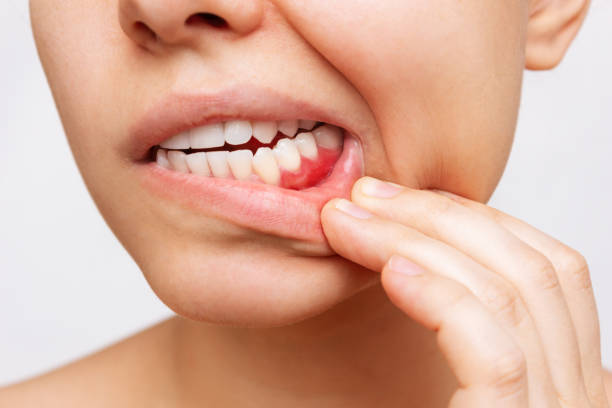
Bleeding gums are often considered a minor issue that can be attributed to poor oral hygiene or gum disease. However, recent research suggests that bleeding gums may be linked to more serious health concerns, including heart disease. Understanding the connection between oral health and cardiovascular health is crucial for taking preventative measures and maintaining overall well-being.
In this article, we’ll explore the potential link between bleeding gums and heart health, the importance of early detection, and steps you can take to protect both your gums and your heart.
What Are Bleeding Gums?
Bleeding gums occur when the soft tissues in the mouth become inflamed and irritated. This condition is often a sign of gum disease, which includes gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease, causes redness, swelling, and bleeding, particularly when brushing or flossing. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress into periodontitis, which can lead to more severe symptoms such as gum recession, tooth mobility, and even tooth loss.
The primary cause of bleeding gums is the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth, which harbor harmful bacteria. These bacteria irritate the gums, leading to inflammation. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, certain medications, and other factors can contribute to the development of gum disease.
The Link Between Bleeding Gums and Heart Health
While gum disease primarily affects the mouth, research has shown that it may also have significant implications for heart health. Studies suggest that the bacteria involved in gum disease can enter the bloodstream through the damaged gum tissues. Once in the bloodstream, these bacteria may contribute to the formation of blood clots, which can increase the risk of cardiovascular problems such as heart attack and stroke.
The connection between bleeding gums and heart disease is believed to be related to the inflammation caused by gum disease. Chronic inflammation is a key factor in the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where the arteries become narrowed and hardened due to the buildup of plaque. Atherosclerosis is one of the leading causes of heart disease, as it restricts blood flow to the heart and other vital organs.
Additionally, some research suggests that the bacteria associated with gum disease may contribute to the formation of fatty deposits in the arteries, further exacerbating the risk of cardiovascular issues. Though the exact mechanism behind this connection is still being studied, there is mounting evidence that taking care of your gums can have a positive impact on your heart health.

The Importance of Oral Hygiene for Heart Health
Given the potential link between bleeding gums and heart disease, maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for overall health. Brushing and flossing regularly are the most effective ways to prevent gum disease and reduce the risk of gum inflammation. Using a toothbrush with soft bristles and fluoride toothpaste can help remove plaque without irritating the gums. Flossing daily is also crucial for cleaning areas between the teeth where bacteria and plaque can accumulate.
Regular dental check-ups are equally important for preventing and treating gum disease. Your dentist can monitor the health of your gums, perform professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar, and provide early intervention if signs of gum disease are present. If you notice symptoms such as bleeding gums, bad breath, or gum sensitivity, it is important to seek dental care promptly to prevent further complications.
In addition to practicing good oral hygiene, it is important to avoid habits that can contribute to gum disease, such as smoking. Smoking not only weakens the immune system but also reduces blood flow to the gums, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections. Maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and getting regular exercise can also support both oral and heart health.
What You Can Do to Protect Your Gums and Heart
Taking steps to protect your gums can also benefit your heart health. Here are some practical tips for maintaining both:
- Brush and floss daily: Good oral hygiene is the foundation for preventing gum disease. Brush your teeth twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Schedule routine dental check-ups and cleanings to monitor your oral health and catch any issues early.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for both gum disease and heart disease. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk.
- Manage chronic conditions: If you have diabetes or other chronic conditions, managing them effectively can help protect both your gums and your heart.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation and support both oral and cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Bleeding gums are more than just a sign of poor oral hygiene; they may also indicate a link to heart disease. Research suggests that the bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream, leading to inflammation that can contribute to cardiovascular problems. By maintaining good oral hygiene, seeking regular dental care, and addressing risk factors such as smoking and diabetes, you can protect both your gums and your heart. Early intervention and preventive care are essential for minimizing the risks associated with bleeding gums and ensuring overall health.